When importing data from various sources into Excel, we may encounter special characters such as punctuation marks, operators, currency symbols, etc. These characters can make it difficult to process data, especially when sorting, filtering, or organizing information correctly.
So, how can we identify special characters in Excel? Is there a formula to find special characters in Excel?. In this article, we will explore three effective methods to detect and remove special characters in Excel.
Nội dung
I. Excel formula to find out special characters in a cell
When working with data in Excel, you may need to check whether a cell contains special characters. This is particularly important when handling serial numbers or ensuring that specific information contains only letters and numbers.
In this guide, we will use Excel formulas to identify special characters. The functions used include SEARCH, ISNUMBER, SUMPRODUCT, and the double negative (--).
Excel formula to find out special characters in a cell
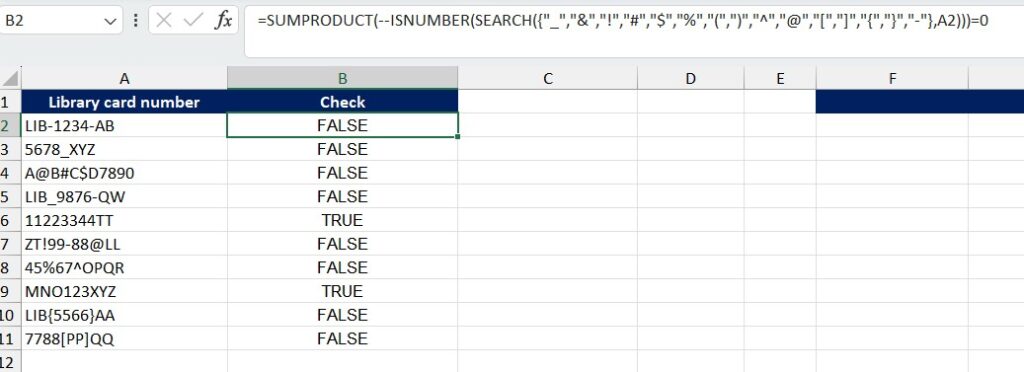
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2)))=0
Step-by-step breakdown of the formula
Step 1: Use the SEARCH function to find special characters
The SEARCH function is used to locate the position of a substring within a larger text string. If found, it returns the position of the first occurrence of that character. If not found, it returns a #VALUE! error.
Formula:
=SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2)
Explanation:
- The array
{"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"}contains the list of special characters to be searched for. A2is the cell being checked.- The function will check for each special character in the list and return its position if found. If not found, it will return an error.
Step 2: Use ISNUMBER to determine the presence of special characters
The ISNUMBER function checks whether a value is a number. If it is a number, it returns TRUE; if not (i.e., an error due to no special character found), it returns FALSE.
Formula:
=ISNUMBER(SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2))
Explanation:
- If
SEARCHfinds a special character, it returns a number (e.g., 3, 5, 7…). - If no special character is found, the result is
#VALUE!. ISNUMBERconverts numbers intoTRUEand errors intoFALSE.
Step 3: Convert TRUE/FALSE into numbers (1 or 0)
Excel treats TRUE and FALSE as logical values. To simplify calculations, we use the double negative (--) to convert them into numbers.
Formula:
=--ISNUMBER(SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2))
Explanation:
- The double negative (
--) convertsTRUEinto1andFALSEinto0.
Step 4: Use SUMPRODUCT to count special characters
The SUMPRODUCT function sums up values in an array. Here, it adds all 1s (if special characters are found) and 0s (if none are found).
Formula:
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2)))
Explanation:
- If
A2contains multiple special characters, each will generate a1in the result array. SUMPRODUCTadds them up, giving the total count of special characters in the cell.
Step 5: Check if a cell contains special characters
To return TRUE if no special characters are found and FALSE if at least one is present, we add =0 to the formula.
Formula:
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH({"_","&","!","#","$","%","(",")","^","@","[","]","{","}","-"},A2)))=0
Explanation:
- If the sum is
0, it means there are no special characters → returnsTRUE. - If the sum is greater than
0, it means at least one special character is present → returnsFALSE.
Step 6: Copy the formula to other cells
After entering the formula in the first cell, you can drag the fill handle down to apply it to other cells and check the entire dataset.
This method provides an efficient way to detect special characters in Excel and ensures data integrity for further processing.
II. How to Find Special Characters in Excel Using VBA
Excel does not have a built-in function to identify special characters, but we can create a User Defined Function (UDF) using VBA to automate this process.
Below is how to create a VBA function to check whether a string contains special characters.
Step 1: Open the VBA Editor
- Open Excel and go to the Developer tab.
- Click Visual Basic to open the VBA editor.
If you don’t see the Developer tab, you can enable it by going to File > Options > Customize Ribbon, then check the Developer option.
Step 2: Insert a New Module
- In the VBA editor, go to Insert > Module to create a new module.
- A new VBA editor window will appear where you can enter the code.
Step 3: Enter the VBA Code to Check Special Characters
Copy and paste the following code into the module window:
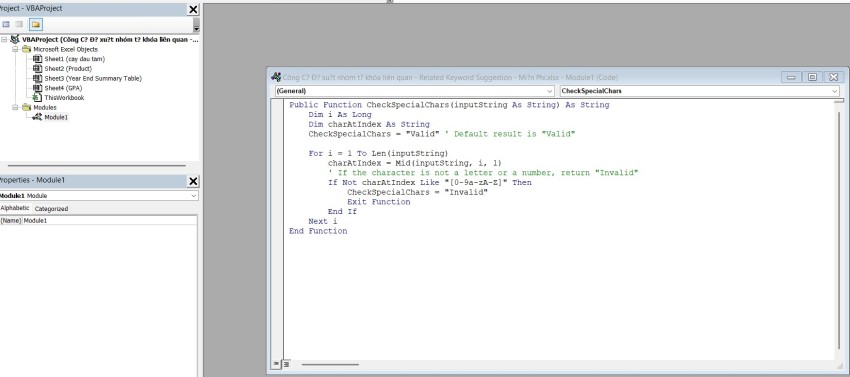
Public Function CheckSpecialChars(inputString As String) As String
Dim i As Long
Dim charAtIndex As String
CheckSpecialChars = "Valid" ' Default result is "Valid"
For i = 1 To Len(inputString)
charAtIndex = Mid(inputString, i, 1)
' If the character is not a letter or a number, return "Invalid"
If Not charAtIndex Like "[0-9a-zA-Z]" Then
CheckSpecialChars = "Invalid"
Exit Function
End If
Next i
End Function
Explanation of the VBA Code
Function Declaration
Public Function CheckSpecialChars(inputString As String) As String
→ Creates a function named CheckSpecialChars that takes an input string from an Excel cell and returns a string result.
Variable Declaration
Dim i As Long, Dim charAtIndex As String
→ Declares i as a loop variable and charAtIndex to store each character being checked.
Default Value
CheckSpecialChars = "Valid"
→ Sets the default return value to “Valid” (meaning no special characters were found).
Loop Through Each Character
For i = 1 To Len(inputString)
→ Loops through each character in the input string.
Extract Characters One by One
Mid(inputString, i, 1)
→ Retrieves each character at position i within the string.
Check for Special Characters
If Not charAtIndex Like "[0-9a-zA-Z]" Then
→ Checks if the character is not a letter or a number. If it’s a special character, it triggers the next step.
Update Result & Exit Function
CheckSpecialChars = "Invalid"
Exit Function
→ If a special character is found, the function immediately returns “Invalid” and stops checking further.
Step 4: Save the File as a Macro-Enabled Workbook
- Press Ctrl + S to save the file.
- In the Save as type field, select Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xlsm).
- Click Save.
If you do not save the file as .xlsm, VBA will not work when you reopen the file.
Step 5: Use the VBA Function in Excel
- In Excel, select an empty cell.
- Enter the following formula to check for special characters in cell A2:
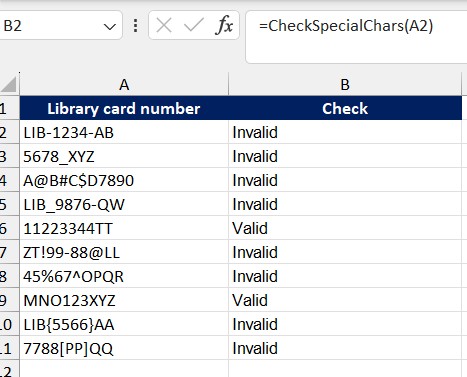
=CheckSpecialChars(A2)
- If A2 contains only letters and numbers, the function will return “Valid”.
- If A2 contains special characters, the function will return “Invalid”.
Using “CheckSpecialChars” instead of “Check” helps avoid conflicts with built-in VBA functions or system variables.
Advantages of Using VBA for Special Character Detection
✔ Quickly and easily checks multiple cells at once.
✔ Automates the verification process without using complex formulas.
✔ Can be reused across multiple Excel files.
III. Using Power Query to Find Special Characters in Excel
Power Query is a powerful tool that allows you to process and transform data without using complex formulas. By leveraging Power Query, we can efficiently identify and remove special characters in Excel.
Step 1: Open Power Query with the Data to Process
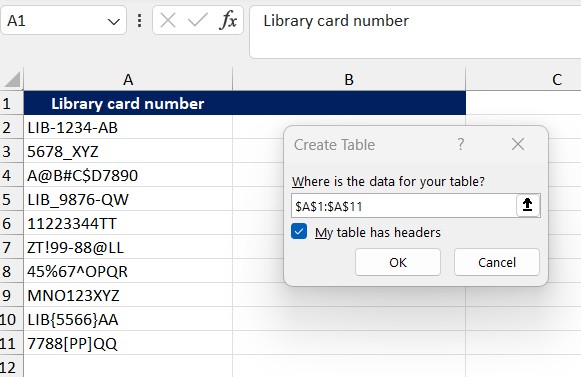
- Select the data range that needs to be checked.
- Go to the Data tab on the toolbar and choose From Table/Range.
- In the Create Table dialog box, ensure the selected range is correct and click OK.
Step 2: Add a Custom Column to Filter Out Special Characters
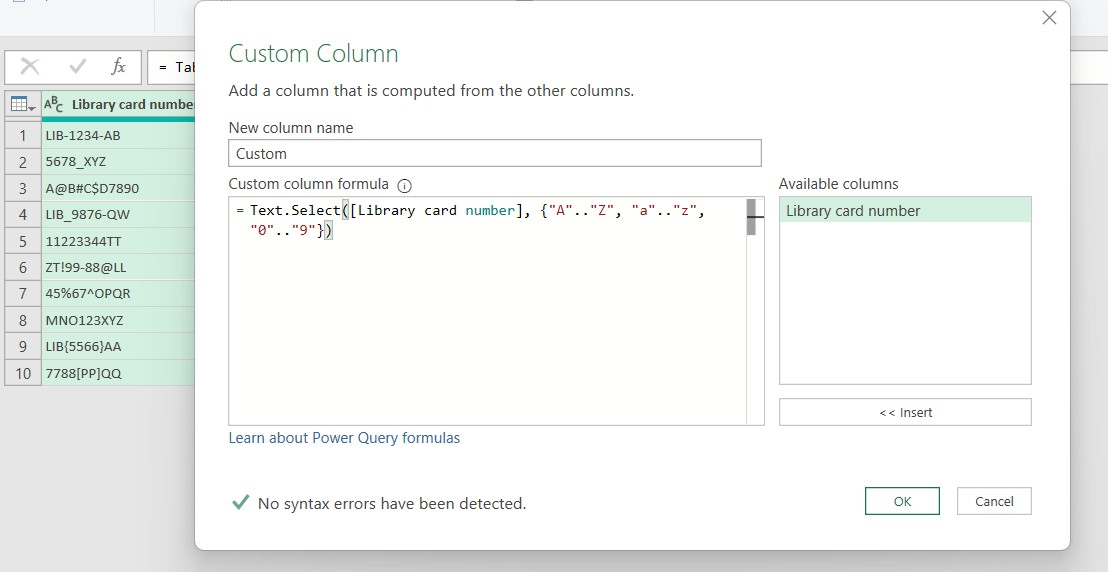
In the Power Query Editor, go to the Add Column tab and select Custom Column.
In the Custom Column dialog box, enter the following formula to remove special characters:
=Text.Select([Library card number], {"A".."Z", "a".."z", "0".."9"})
Click OK to apply the formula.
Explanation of the Formula:
Text.Select(): A Power Query function used to filter characters based on a given condition.[Library card number]: The column containing the data to be processed. (Replace it with the column you need to process).{"A".."Z", "a".."z", "0".."9"}: A set of valid characters, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers from 0 to 9.- This formula retains only valid characters and removes all special characters.
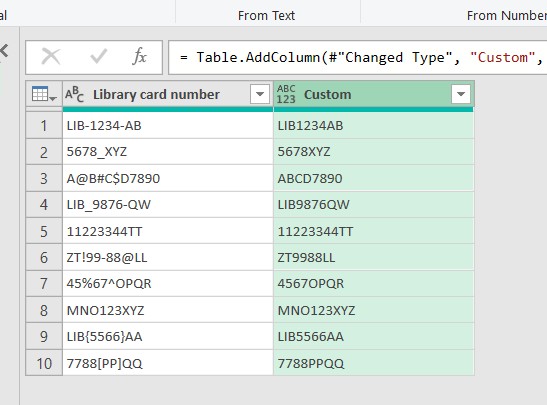
Step 3: Finalize and Load Data Back to Excel
- Review the results in the new column.
- Go to the Home tab and click Close & Load to return the processed data to Excel.
- Once completed, the new data table will no longer contain special characters, making it easier for you to analyze and manage your data.
Using Power Query is also one of the methods to remove special characters in Excel effectively.
Conclusion
Finding and removing special characters in Excel is crucial to ensuring accurate and easily manageable data. We can apply one of the three methods discussed above to detect special characters in Excel.
In particular, using the Excel formula to find special characters in a cell allows for a quick and efficient search.
We hope this article helps you understand how to find special characters in Excel and apply it to your work. Good luck!